Symptoms &
complications
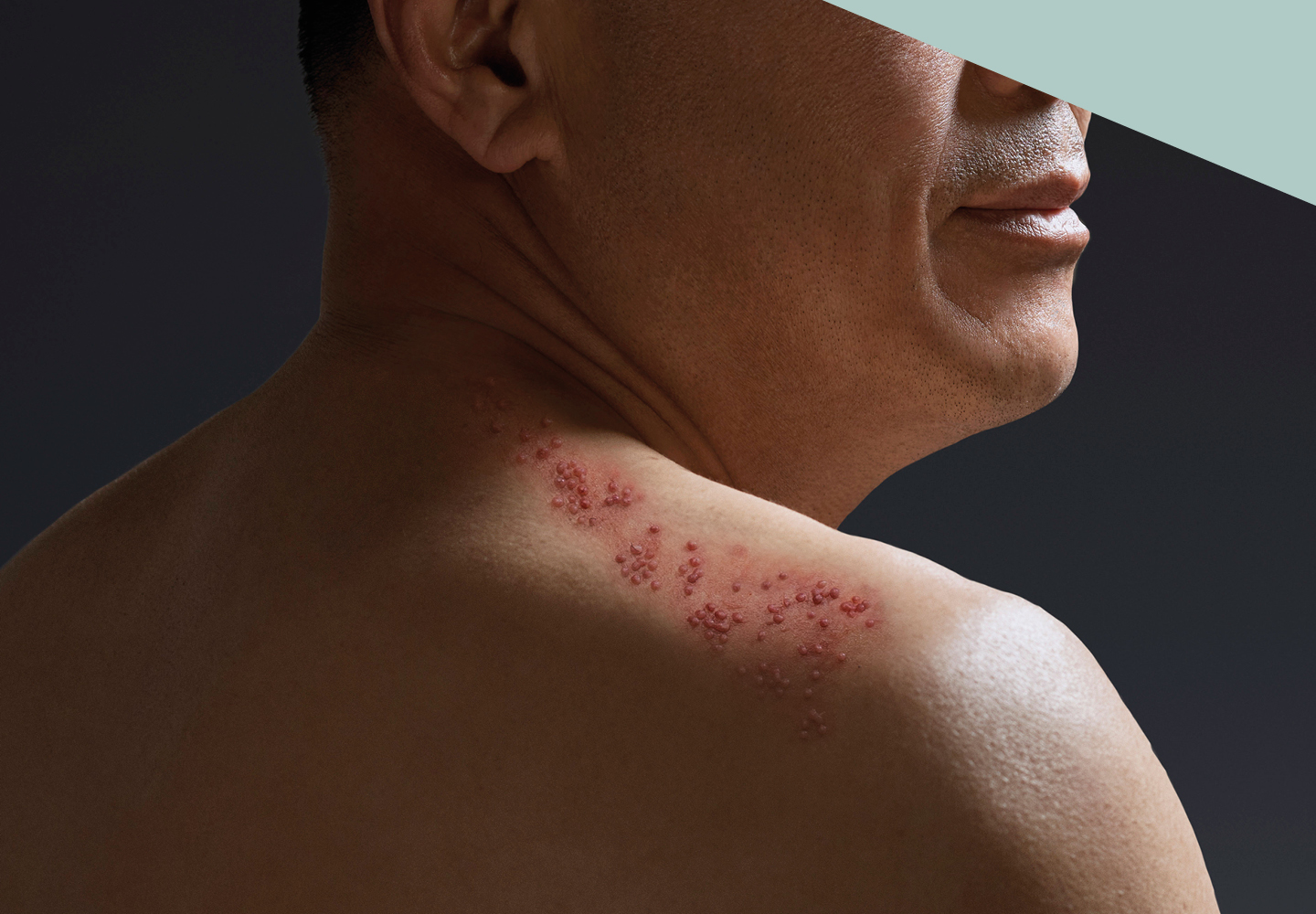
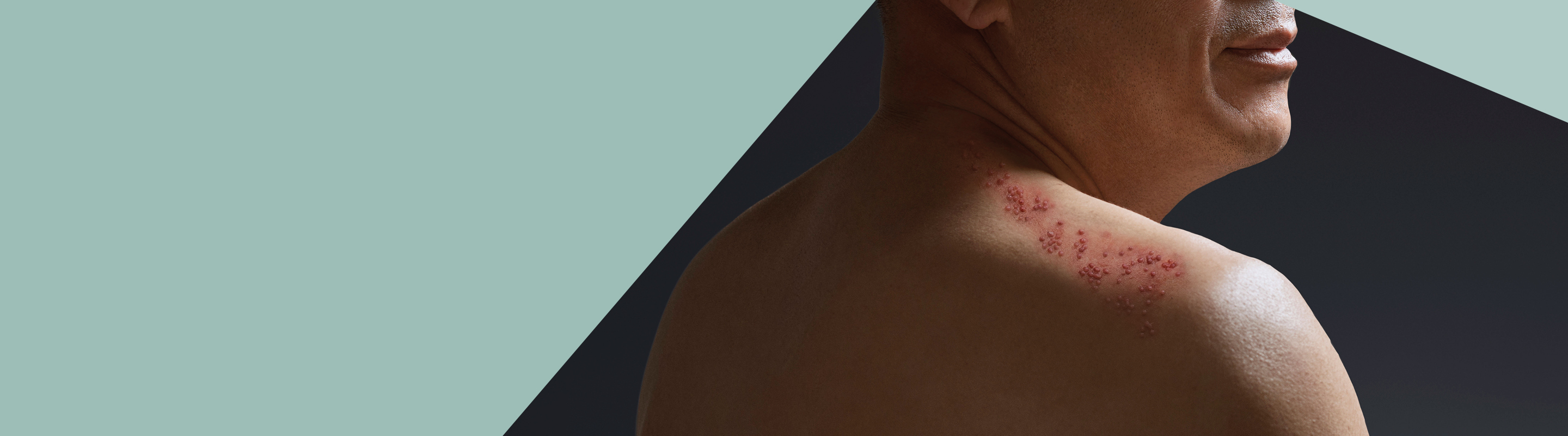
The first signs and symptoms of shingles can be a tingling or painful feeling in an area of skin, a headache or feeling generally unwell.
Typically, a blistering rash may appear a few days later, on one side of the body only. The shingles rash most commonly appears on the chest or abdomen, but can appear anywhere on the body including the face. It can take up to 4 weeks for the rash to heal.
If you think you may have shingles, please seek prompt medical attention.
Possible complications of shingles
Some people may experience complications. These include:

Post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN):
The most common complication of shingles is post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN) which is nerve pain that persists after the shingles rash has healed. PHN typically lasts for three to six months but can persist for longer. It can be more common and more severe in older people than in younger people. After the age of 50 years, about 20% of patients with shingles will develop post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN).
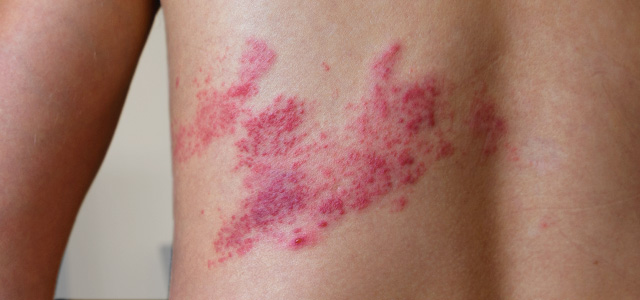
Skin changes:
Skin changes such as scarring and changes in pigmentation can occur after a shingles rash has healed.
Secondary infection of the rash can also occur.
Neurological and cardiac problems:
Neurological complications such as encephalitis (swelling of the brain) and cardiac complications such as stroke and vascular disease (conditions affecting the blood vessels) are rare but can occur as a complication of shingles.

Vision and hearing problems:
In some cases the virus can affect nerves in the face and around the eyes. This can lead to hearing, and vision problems which if left untreated can in rare cases, lead to blindness.
This is not an exhaustive list of complications which can arise from shingles. Please speak to a healthcare professional for more information.
The Shingles National Immunisation Programme is a NHS vaccination programme to help protect against shingles.
Find out more and check eligibilityFurther resources
A selection of GSK resources which contain information about the National Immunisation Programme eligibility can be found here.
More information
If you’re still unsure about your eligibility or you want to learn more about shingles and the Shingles National Immunisation Programme, speak to your nurse or GP surgery.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects following vaccination, talk to your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in the package leaflet.
You can also report side effects directly via the Yellow Card Scheme Website: yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of medicines.
References
- NHS. Shingles. 2023.
- DH Green Book Ch 28a. Shingles. 2024.
- NICE Clinical Knowledge Summaries. Shingles: What are the complications. 2024.
- Gauthier A et al. Epidemiol Infect. 2009; 137: 38-47.
